git and github
What is Source Code Management ?
Source code management is like a digital filing system for computer code. It helps developers work together on projects by keeping track of changes they make to the code. It saves different versions, lets people work on separate parts at the same time, and shows who did what and when. Popular tools include Git, which makes it easy to manage code changes and collaborate with others.
Types of Source Code Management
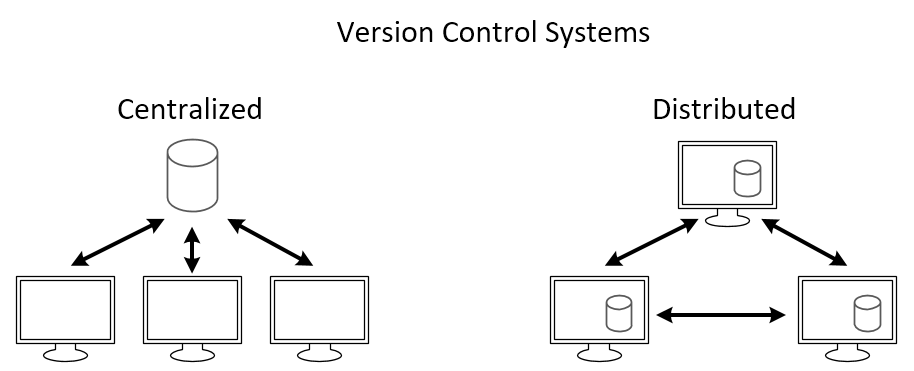
There are mainly two types of source code management: centralized and distributed.
Centralized Source Code Management
In this type, there is a central server that stores the code repository, and developers check out code from this central location to work on it.
Benefits of Centralized Source Code Management
Centralized systems make teamwork easier by keeping all the project’s code in one place, controlling who can make changes, tracking those changes over time, and providing a clear history.
Drawbacks of Centralized Source Code Management
Single Point of Failure: If the central server goes down, developers may lose access to the repository.
Limited Offline Capabilities: Often require a stable internet connection.
Difficulty with Branching and Merging: Can be complex and prone to conflicts when multiple developers work simultaneously.
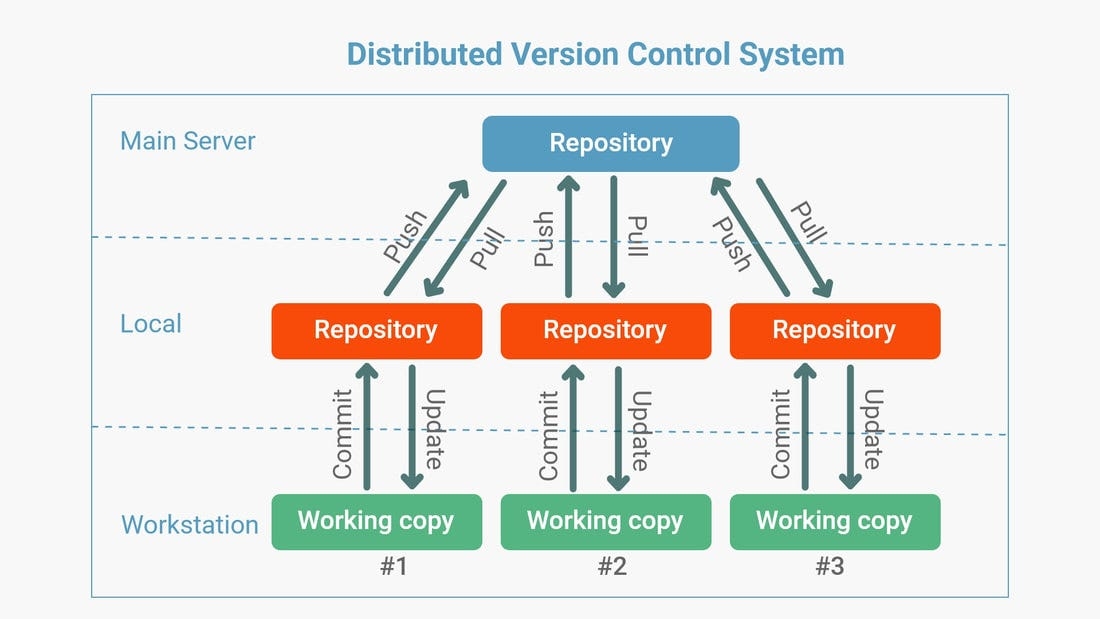
Distributed Source Code Management
Here, every developer has a local copy of the entire repository, including its history. Developers can work independently on their local copies and then share changes by pushing them to a central server or directly to other developers. Git and Mercurial are popular DSCM tools.
Benefits of Distributed Source Code Management
Flexibility: Work offline and independently on local copies.
Improved Collaboration: Share changes directly with others without always relying on a central server.
Reduced Dependency on Internet: Can work offline and sync later.
In this blog, we'll explore Git, the famous distributed version control system, and GitHub, which offers online storage and collaborative features for managing code projects.
What is Git ?

Git is a tool that helps developers keep track of changes they make to their code. It’s like a time machine for your projects, letting you see what you’ve done and work with others easily.
To install Git, click here to go official Git installation page: https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Getting-Started-Installing-Git
Git Workflows
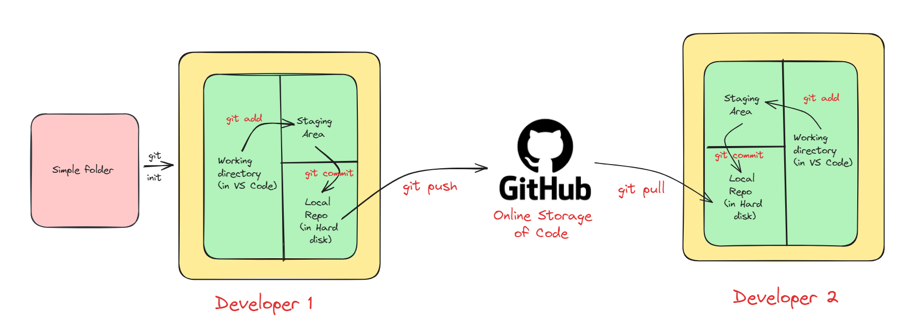
The image below illustrates the workflow used with Git and GitHub.
Local repository: Your project’s files stored in a folder on your computer.
Working directory: Where you actively make changes to project files.
Staging area: Temporarily store changes before saving them.
Commit: Saving a snapshot of changes with a message (git uses SHA-1 checksum for tracking).
Local repository (on hard disk): All your commits are permanently stored on your computer.
GitHub repository (online): A copy of your local repository on GitHub’s servers.
Push: Sending local commits to GitHub.
Pull: Getting the latest changes from GitHub to your local repository.
Live Demo of Git
Create repository and initialize Git
Create a folder at your desired location (e.g., a folder named demo). Open the terminal inside VS Code and run:
Create and stage a file
Create a file (e.g., demo.txt) and add some content. Then stage changes:
Push to GitHub
Create a repository on GitHub first. Then link and push from your terminal:
git remote add origin https://github.com/sachin0612/demo.git git branch -M main git push -u origin main
