Load-balancing algorithms
Load-balancing algorithms for the back-end services.
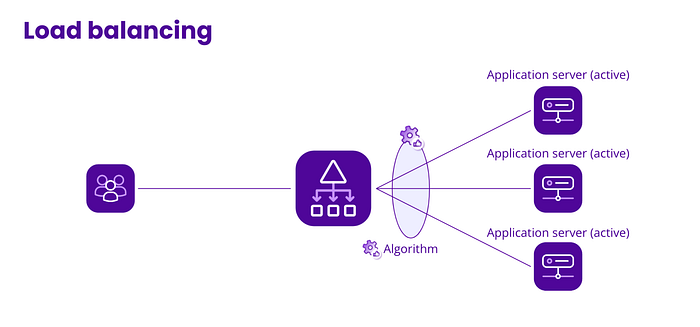
1.Round-Robin : It is the default mode. 2. Least connection: (smallest number of open connections) 3. Weighted Round Robin.(assign the request on the bases of back-end’s server configuration.) 4. IP hashing.(route the request of a user to specific server only to maintain the sessions) 5. Random.(randomly assign the request on the available back-end server) 6. Least Response Time.(assign the request with the least response time) 7. Adaptive Load Balancing. (Dynamically adjust the load balancing on the bases of monitoring).
Load-balancing algorithms are techniques used to distribute incoming network traffic across multiple back-end servers or resources. Here are some commonly used load-balancing algorithms for the back-end:
1. **Round Robin**: In this algorithm, each incoming request is sequentially assigned to the next available backend server in a rotating manner. It evenly distributes the traffic across all servers in a cyclic order.
2. **Least Connection**: This algorithm assigns new requests to the back-end server with the fewest active connections at that time. It helps distribute the load more evenly by considering the current workload of each server.
3. **Weighted Round Robin**: Similar to the Round Robin algorithm, but with the ability to assign different weights to each back-end server. Servers with higher weights receive a larger proportion of the traffic, allowing for better load distribution when servers have different capacities
4. **IP Hash**: This algorithm uses the client’s IP address to determine which backend server to route the request to. It ensures that requests from the same client are consistently routed to the same server, which can be useful for session persistence or caching scenarios.
5. **Random**: In this algorithm, requests are assigned randomly to any available backend server. While it is simple to implement, it may not provide optimal load balancing in all cases.
6. **Least Response Time**: This algorithm tracks the response time of each backend server and assigns new requests to the server with the lowest response time. It aims to distribute the load based on the server’s current performance.
7. **Adaptive Load Balancing**: This algorithm dynamically adjusts the load-balancing strategy based on real-time monitoring of server performance metrics. It adapts to changing conditions and may use a combination of different algorithms depending on the current load and server health.
Last updated
